Chipsets
- A number of integrated circuits designed to perform one or more related functions. For example, one chipset may provide the basic functions of a modem while another provides the CPU functions for a computer.
- Newer chipsets generally include functions provided by two or more older chipsets. In some cases, older chipsets that required two or more physical chips can be replaced with a chipset on one chip.
- The term is often used to refer to the core functionality of a motherboard.
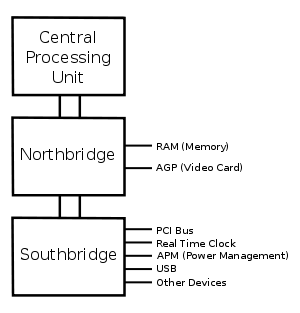
Diagram of the motherboard chipset
NORTHBRIDGE
-
The northbridge, also known as a memory controller hub (MCH) or an integrated memory controller (IMC) in Intel systems (AMD, VIA, SiS and others usually use 'northbridge'), is one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a PC motherboard, the other being the southbridge.
-
Separating the chipset into the northbridge and southbridge is common, although there are rare instances where these two chips have been combined onto one die when design complexity and fabrication processes permit it.,
-
The Southbridge, also known as an I/O Controller Hub (ICH) or a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) in Intel systems (AMD, VIA, SiS and others usually use 'southbridge'), is a chip that implements the "slower" capabilities of the motherboard in a northbridge/southbridge chipset computer architecture.
- The southbridge can usually be distinguished from the northbridge by not being directly connected to the CPU. Rather, the northbridge ties the southbridge to the CPU.
A typical north/southbridge layout
Chipset Characteristics
The characteristics of a chipset can be broken down into six categories: host, memory, interfaces, arbitration, south bridge support, and power management. Each of these categories defines and differentiates one chipset from another. The characteristics defined in each of these categories are as follows:
• Host This category defines the host processor to which the chipset is matched along with its bus voltage, usually GTL+ (Gunning Transceiver Logic Plus) or AGTL+ (Advanced Gunning Transceiver Logic Plus), and the number of processors the chipset will support.
• Memory This category defines the characteristics of the DRAM support included in the chipset, including the DRAM refresh technique supported, the amount of memory support (in megabits usually), the type of memory supported, and whether memory interleave, ECC (error correcting code), or parity is supported.
• Interfaces This category defines the type of PCI interface implemented and whether the chipset is AGP compliant, supports integrated graphics PIPE (pipelining), or SBA (side band addressing).
• Arbitration This category defines the method used by the chipset to arbitrate between different bus speeds and interfaces. The two most common arbitration methods are MTT (multi transaction timer) and DIA (dynamic intelligent arbiter).
• South bridge support All intel chipsets and most of the chipsets for all other manufacturers are two processor sets. In these sets the north bridge is the main chip and handles CPU and memory interfaces among other tasks, while the south bridge (or the second chip ) handles such things as the USB and IDE interfaces, the RTC (real time clock),and support for serial and parallel ports.
• Power management All intel chipsets support both the SMM (system management mode) and ACPI (advanced configuration and power interface power management standards).